Solar Activity:

The sun is a magnetic variable star that fluctuates on times scales ranging from a fraction of a second to billions of years.
Solar flares, coronal mass ejections, high-speed solar wind, and solar energetic particles are all forms of solar activity. All solar activity is driven by the solar magnetic field.
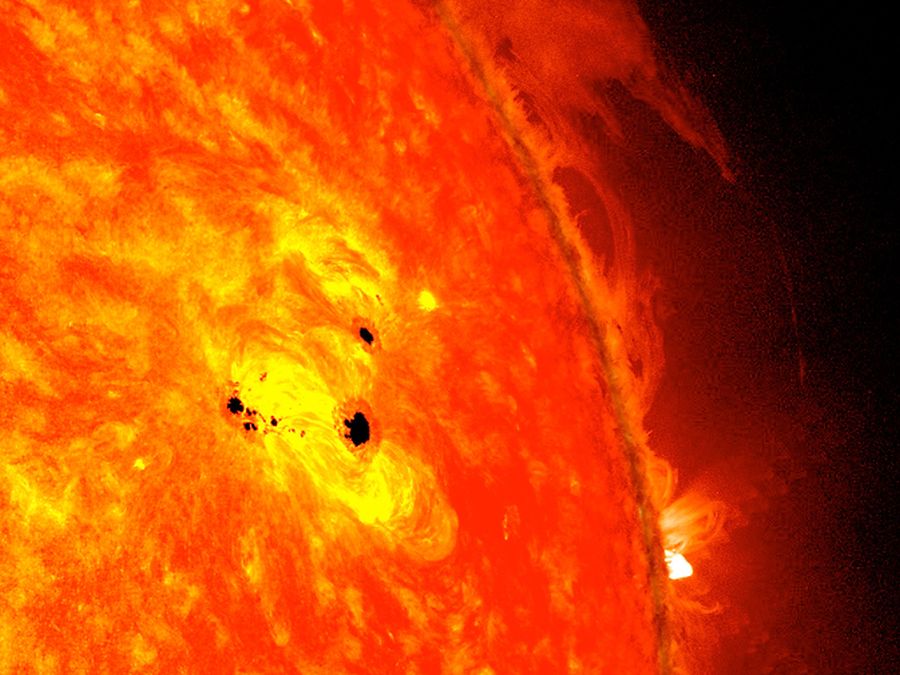
Sun spots:
There are some well defined regions on Sunís surface that appear darker than their surroundings because of lower temperature and are called as sunspots.
Solar flares:
ejects great quantity of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation called solar flares and more powerful solar flares i.e. coronal mass ejections. The energy released during a flare is typically ten million times greater than the energy released from a volcanic explosion
Coronal mass ejections (CME):
In a CME plasma is emitted from the active centre, sometimes over a large region of solar surface that may span longitudinal intervals of more than 90 degree. The CMEs carry magnetic fields along with, which tends to fill the heliosphere (the magnetically closed region around the solar system).
High-speed solar wind streams
The solar wind continuously flows outward from the Sun and consists mainly of protons and electrons in a state known as a plasma. ... Coronal holes produce solar wind of high speed, ranging from 500 to 800 kilometers per second.
Solar energetic particles:
Solar energetic particles (SEP) are high-energy particles coming from the Sun. They were first observed in the early 1940s. They consist of protons, electrons and HZE ions with energy ranging from a few tens of keV to many GeV